Embedded MotherboardS
Embedded motherboards are basically constructed like mainboards in standard PCs. They offer processor sockets, RAM slots, BIOS chip with integrated firmware, interface modules and slots for expansion cards. However, they are optimized for the requirements of embedded applications, for example for installation in special housings for industrial use in the form factors m-ITX, ATX, Flex-ATX and Micro-ATX. An additional feature is the long-term availability of up to seven years.
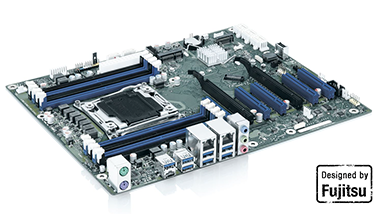
ATX motherboards have the possibility to support up to 7 expansion slots thanks to the 305 x 244 mm dimensions. ATX motherboards are suitable for many industrial applications.
Another form factor of the embedded motherboards is FLEX ATX (229 mm × 191 mm). Compared to m-ITX, this form factor offers an even greater variety of interfaces.
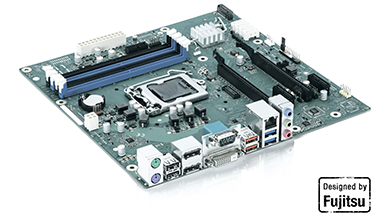
MicroATX motherboards are only 244 x 244 mm and use the same power connector as ATX motherboards and are compatible with processors from leading manufacturers.
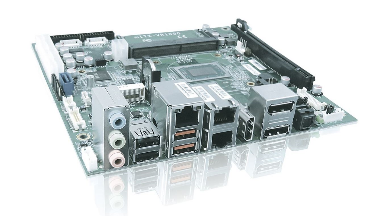
Measuring a mere 147 x 140 mm in size, the Mini-STX offers a compact form factor with the flexibility to upgrade processors and a wide range of connectivity options. These systems are designed to provide efficient, powerful, and eco-conscious computing solutions.
ATX motherboards have the possibility to support up to 7 expansion slots thanks to the 305 x 244 mm dimensions. ATX motherboards are suitable for many industrial applications.
Another form factor of the embedded motherboards is FLEX ATX (229 mm × 191 mm). Compared to m-ITX, this form factor offers an even greater variety of interfaces.
MicroATX motherboards are only 244 x 244 mm and use the same power connector as ATX motherboards and are compatible with processors from leading manufacturers.